- Home
- Deck Boards
- KAPUR decking
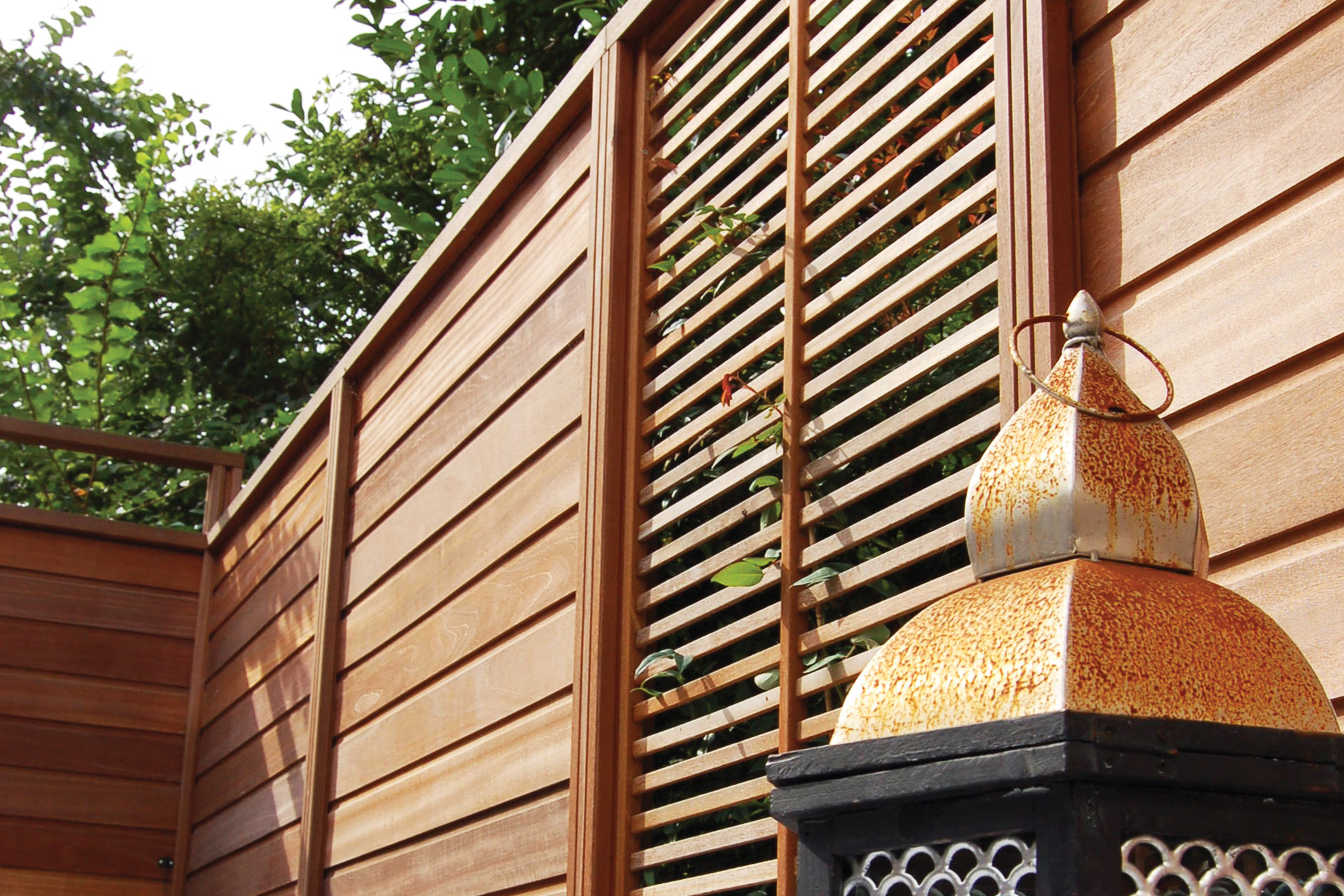
KAPUR decking
A board with light and homogeneous shades
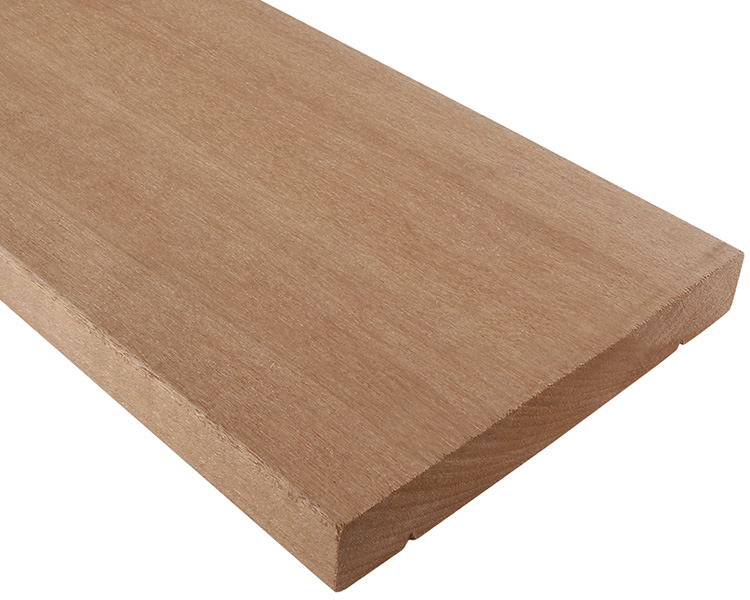


- Colour brown-red
- Light cross grain
- Good durability
- Stable
A sustainable essence for outdoor construction
Kapur, botanical name Dyrobalanops spp. is a wood from Southeast Asia. Renowned for its durability, Kapur is a hardwood used for outdoor constructions. It has a fairly wide range of applications. It is a timber used in exterior joinery, particularly for door and window sills and deck boards, as it is resistant to rot when exposed to the weather.
It is increasingly used as a substitute for Bangkirai. Kapur is initially reddish-brown to orange and darkens rapidly to brown under the influence of UV light.
Our Kapur comes from tropical forests in the lowlands of Indonesia. The trees can reach 60 m high with a diameter of 80 to 100 cm. Well-formed buttresses support their straight, cylindrical shaft and the trunk is free of branches up to 30 m high, which explains their homogeneity.
When freshly cut, the wood gives off an odour of camphor which disappears when drying
- Smooth : 21x145 ; 25x145 ; 27x190 mm
- Grooved : 21x145 ; 25x145 mm
Characteristics
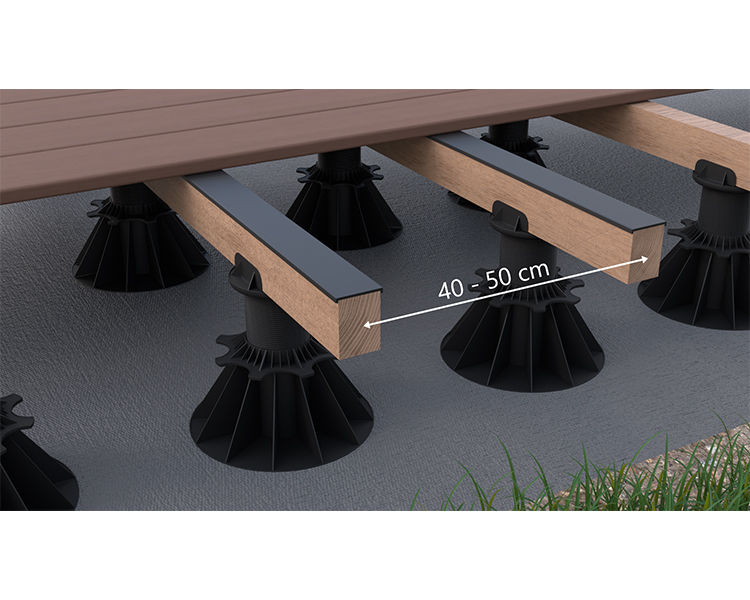

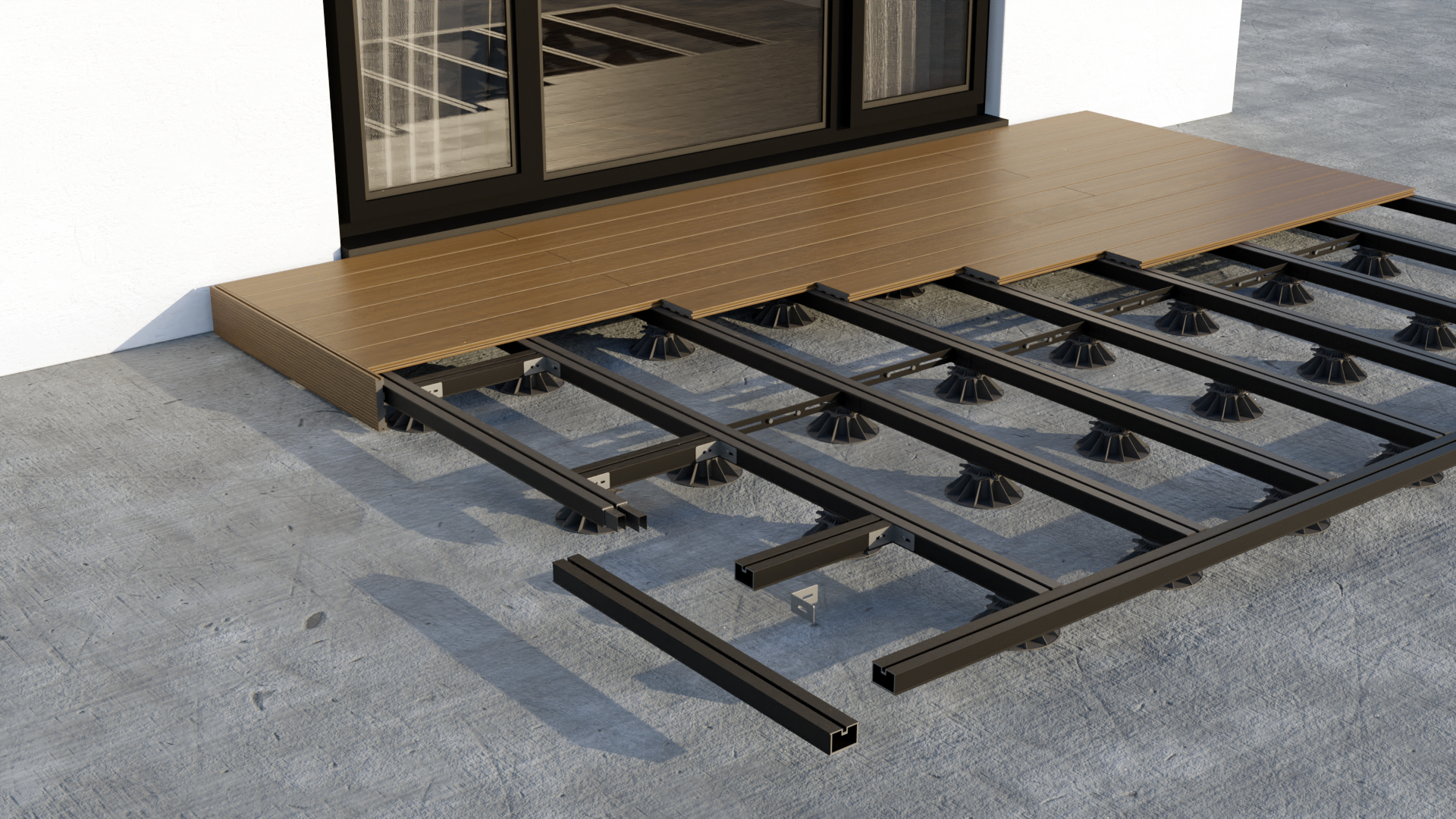
Installation of the joists
Plan a centre-to-centre distance of between 40 and 50cm between joists. This distance is specified for each of our profiles in the attached table.
The joists must be laid with a slope of 2% in the longitudinal direction of the boards to allow rainwater to run off. This 2% slope must be strictly observed!
Water must also be able to flow under the structure. The joists must be supported on rubber pedestals or supports.
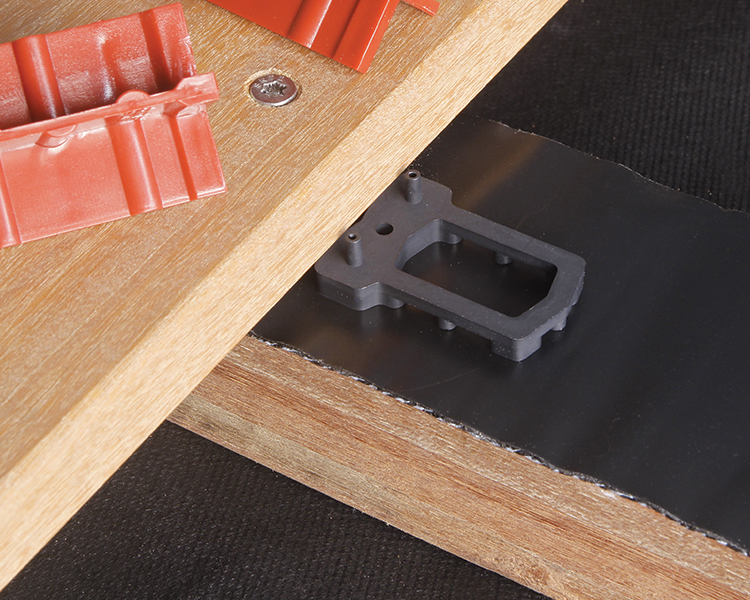
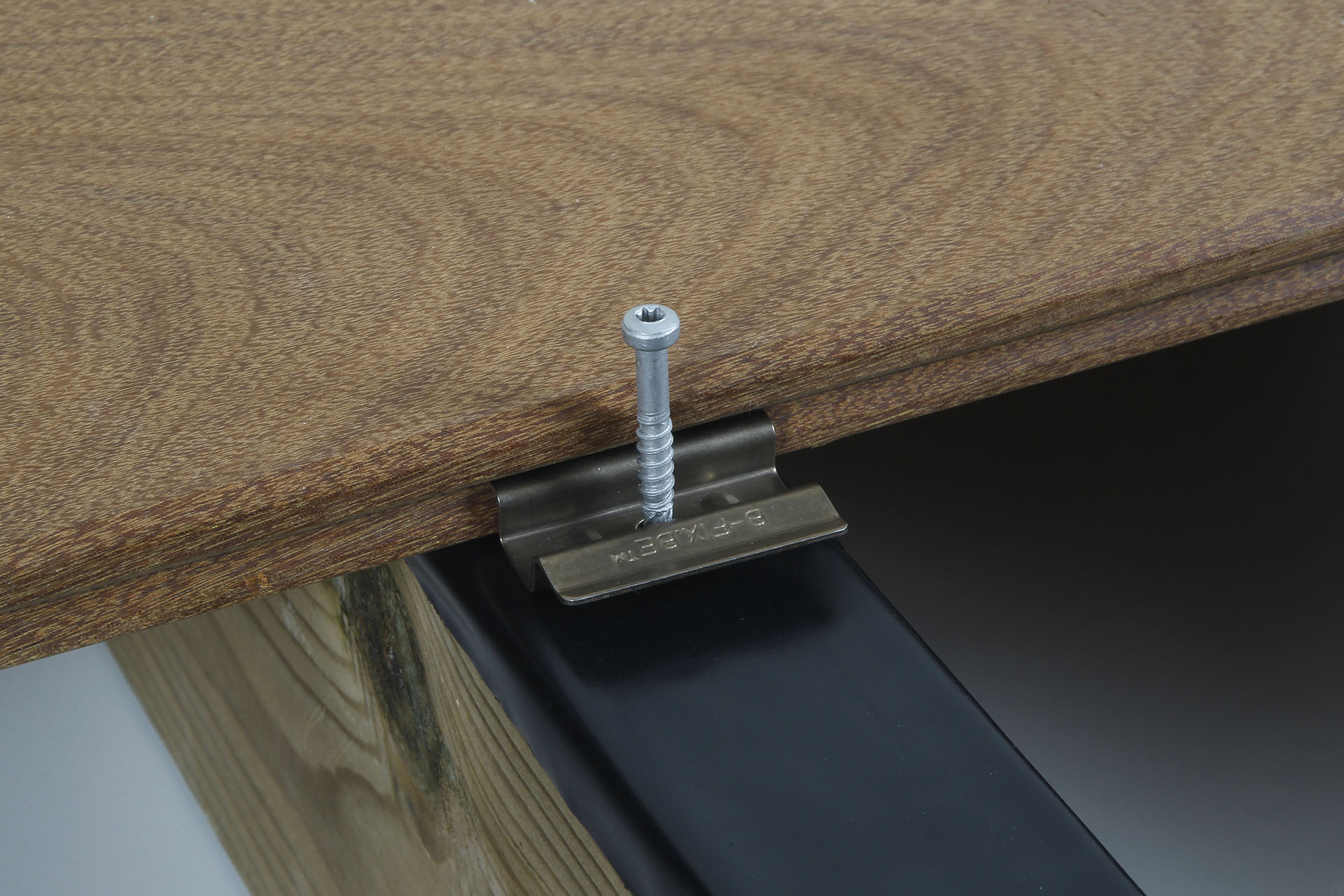
Protect your joists and increase their lifespan: Use the Bitudeck bitumen strip to cover the joists and prevent water infiltration at the fastening points.
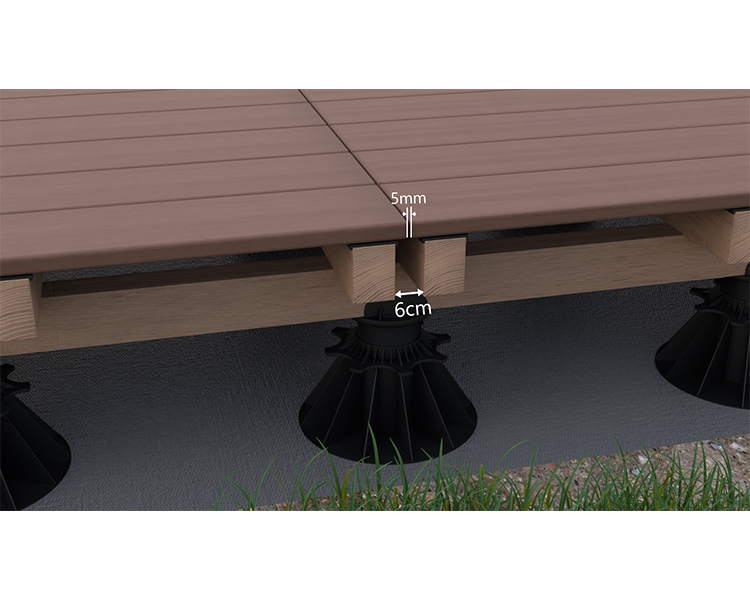

Double joisted and cross joisted
Double joisting allows for water to flow between board extremities. Distance between board extremities must be between 4 and 6 mm and distance between the end of the boards and the joist must be between 20 and 30 mm.
Cross joisting
For a faster and longer lasting installation, we recommend cross joisting.
A layer of joists is fixed perpendicularly on a first layer of rafters. The flatness of the deck is easier and quicker to adjust, and ventilation is improved.
In the case of loose and poorly stabilised soil, we recommend the use of galvanised steel foundation screws to ensure effective and durable anchoring of your deck.
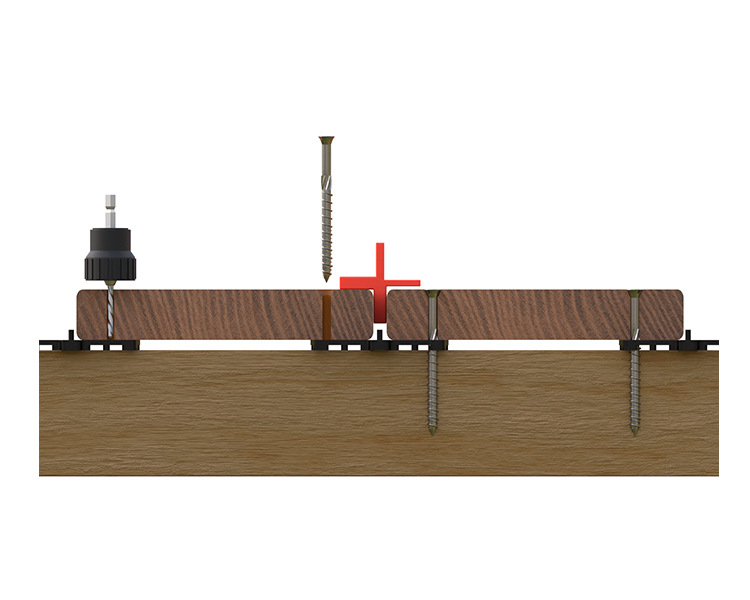
Fixing the boards to the wooden joists
Spacing between the decking boards should be kept between 5 and 7mm (taking into account a wood moisture content of 14-16% at delivery). Use board spacers during installation.
| Humidity of the boards | from 12 to 17% | from 18 to 22% | > 23% at H > PSF |
| Thickness of the spacer shim | 7 or 6 mm | 5 or 4 mm | 3 or 2 mm |
To avoid water being trapped between the boards and the joists, we recommend the use of a ventilation wedge of the Airspacer type. Air circulation under the boards prevents any moisture settling.
Ensure good ventilation of the boards
Never completely close the skirts of the deck to "let the air circulate". Leave a ventilation space of 2 cm between floor and skirting. The minimum space between the decking boards and the ground should be 4 cm to 10 cm for damp floors.
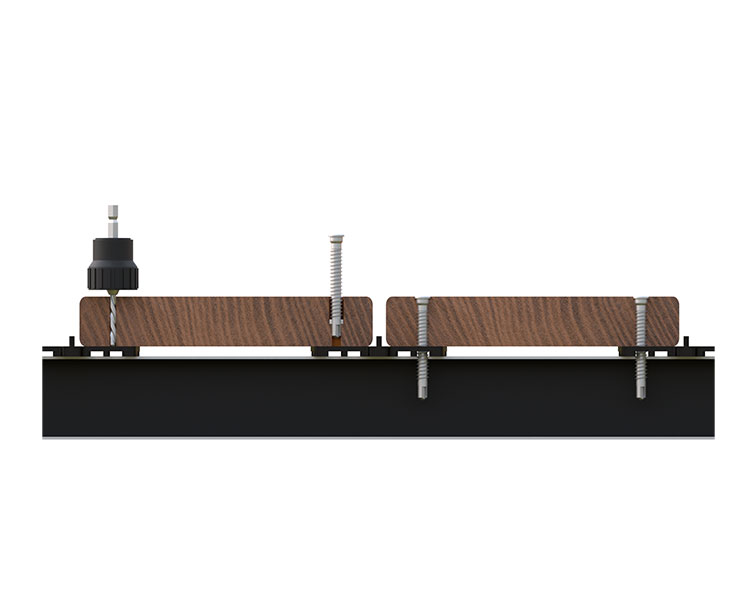

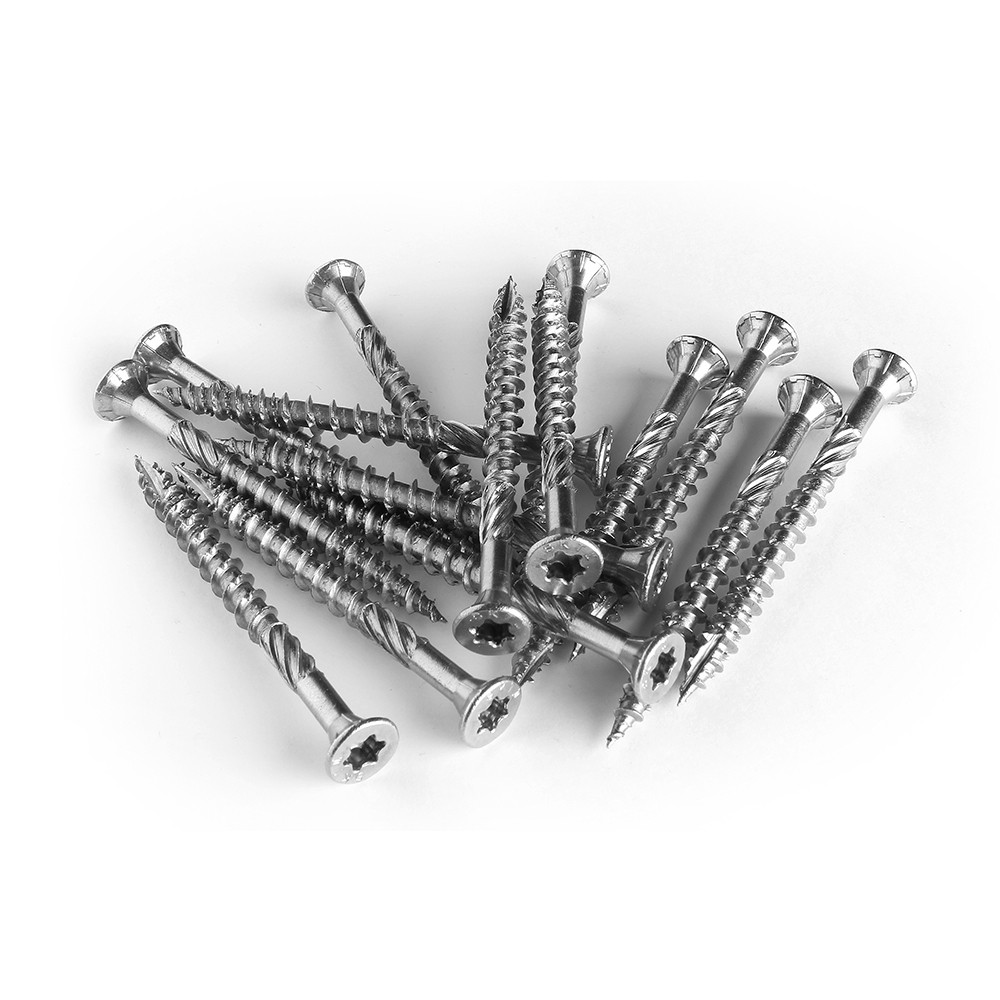
Screw-mounting boards to aluminium joists.
Two stainless steel screws are required per fixation point. Use metallic self drilling screws. The board must be pre-drilled with the same drill bit diameter or even slightly larger than the screw diameter + countersink. The upper bare side of the countersunk screw must be slightly smaller than the upper side of the board (2mm).
The distance between the edges of the board is 1.5 to 2 cm. Always fix the ends of the boards less than 5 cm from the edge.
To limit noise pollution and reduce shearing effect on the screws due to aluminium expansion, we recommend applying a 5mm thick Shore 15 EPDM tape to the joists.
All FelixWood woods comply with the European Union Forest Law Enforcement, Governance and Trade Regulation (EU FLEGT). We scrupulously check the certificates of origin of the forest plots. All stages of production, from tree to shipment of the wood are traced and identified. We ensure continuous audit of all our suppliers in accordance with EU FLEGT. As such, 100% of our timber is of legal origin.
But beyond that, we are significantly increasing the proportion of our FSC-certified wood every year.
Tropical forests are subject to constant pressure from local populations and economic actors. 13 million hectares of tropical forest are disappearing every year, to be transformed into agricultural or breeding land, but also to use wood as a simple fuel for cooking food.
FelixWood shares FSC® values as described in the "Policy for Association of Organisations with FSC" (FSC-POL-01-004, July 2009).
When buying FSC-certified FelixWood timber, you can be sure you are helping the local population taking care of its forest, ensuring its subsistence and its regeneration according to strict legal rules. For more information click here.
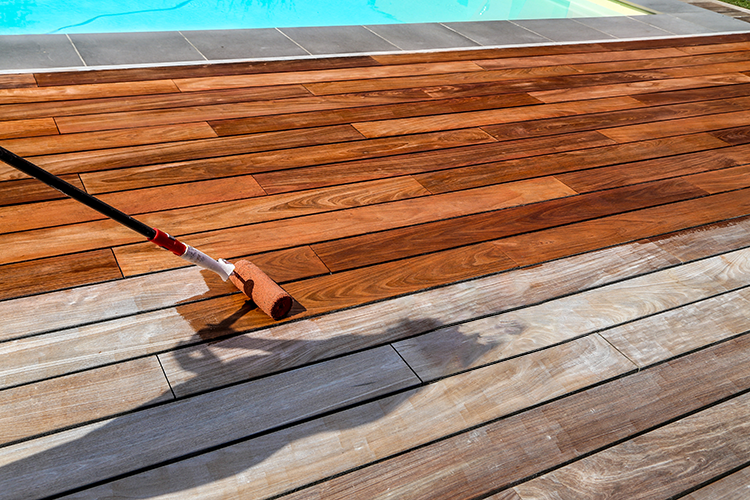

Maintenance of KAPUR boards
Wood turns grey and the surface cracks due to the weather. We recommend oiling the surface, thereby reducing these effects. Only use non water-based non film-forming oils.
Caution: check in advance whether the oil is suitable for the type of wood used. Application of the oil is necessary at least once a year or even several times, depending on location and weather conditions.
After the winter, clean your decking against moss, which represents an increased slippery risk. Never clean with a high-pressure jet.
CAUTION : The appearance of black spots is quite common. These spots, grey or black, spike shaped, are often mistakenly confused with mould. This is a fine metal particles oxidation reaction on the surface of the wood. They can come from a variety of sources (lawn fertilizer, plaster and cement, metal dust from cutting work, etc.). This phenomenon can occur suddenly, after moisture deposit on the deck (dew, rain, etc.).
If this happens, see the information sheet: iron oxide / oxalic acid reaction.






